WIKI Attractors and oscillators
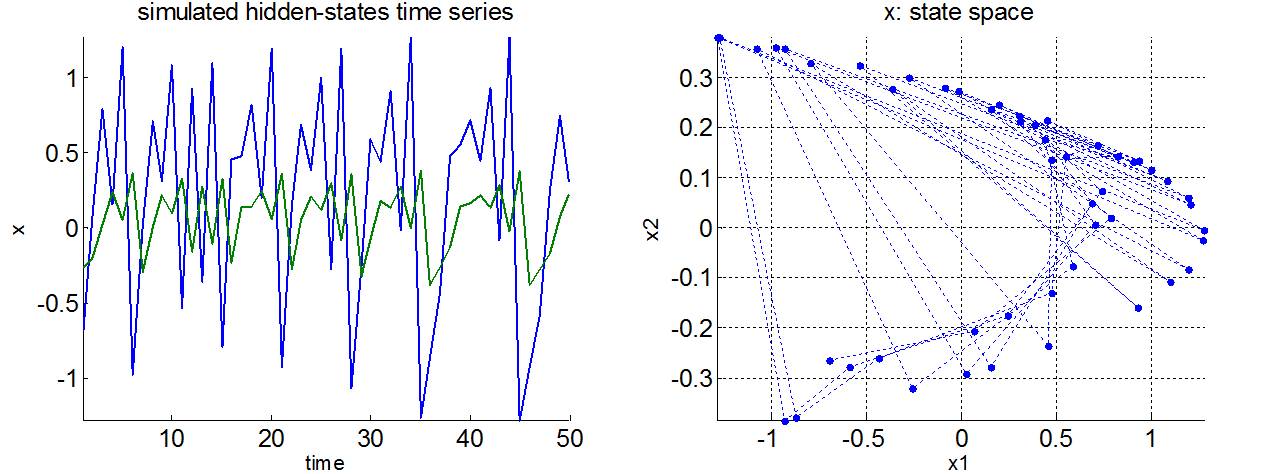
Van der Pol oscillator
This model captures the essence of action potential dynamics, which essentially consist in stereotypical responses to perturbations, i.e. a stable limit cycle. See demo_VanDerPol.m.
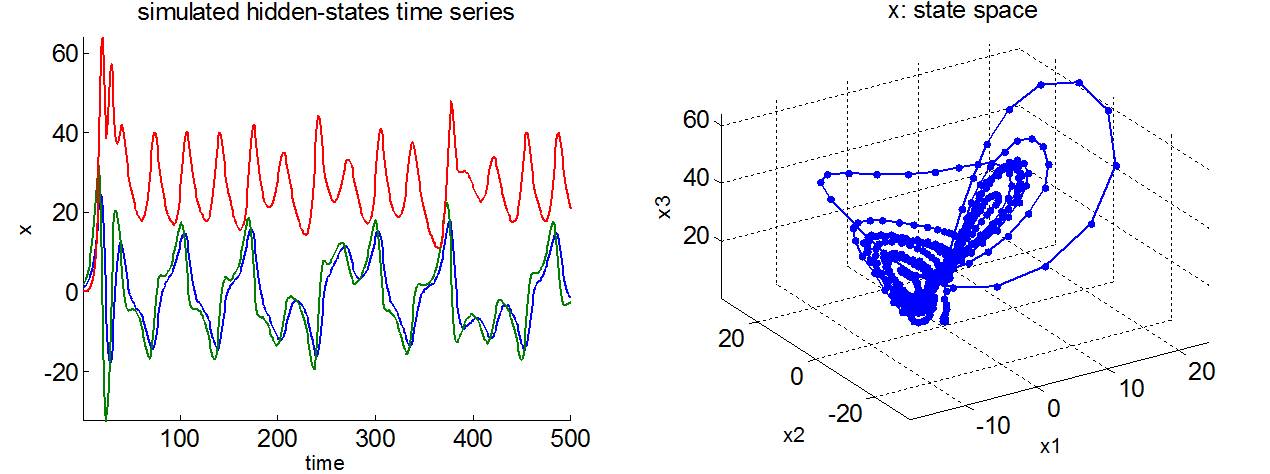
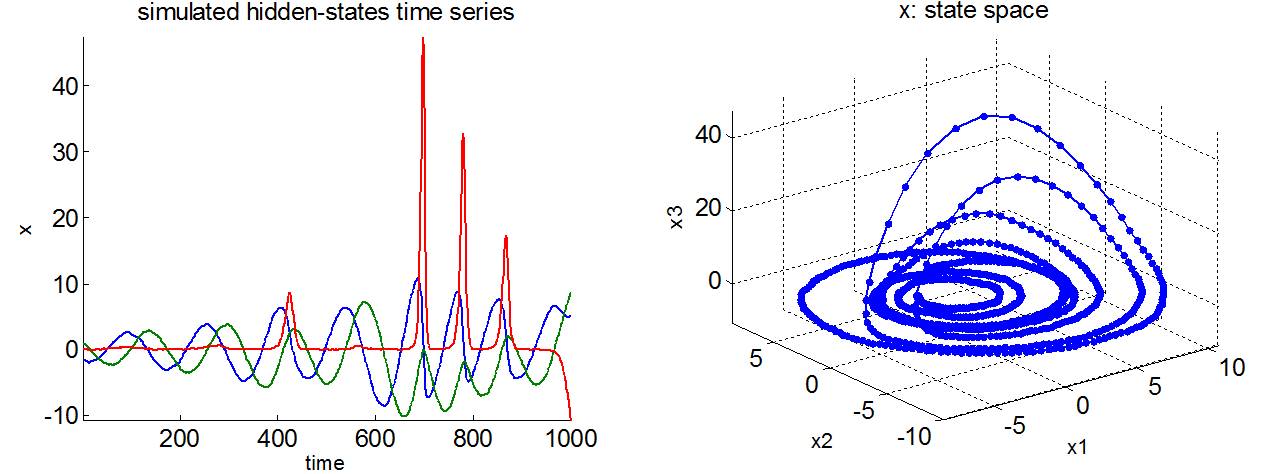
Lorenz attractor
The Lorenz attractor was originally proposed as a simplified version of the Navier-Stokes equations, in the context of meteorological fluid dynamics. The Lorenz attractor models the autonomous formation of convection cells, whose dynamics are parameterized using three parameters: the Rayleigh number (which characterizes the fluid viscosity), the Prandtl number (which measures the efficacy of heat transport through the boundary layer) and a dissipative coefficient. When the Rayleigh number is bigger than one, the system has two symmetrical fixed points , which act as a pair of local attractors. For certain parameter values, the Lorenz attractor exhibits chaotic behaviour on a butterfly shaped “strange attractor”. For almost any initial conditions (other than the fixed points), the trajectory unfolds on the attractor. The path begins spiralling onto one wing and then jumps to the other and back in a chaotic way. See demo_Lorenz.m.
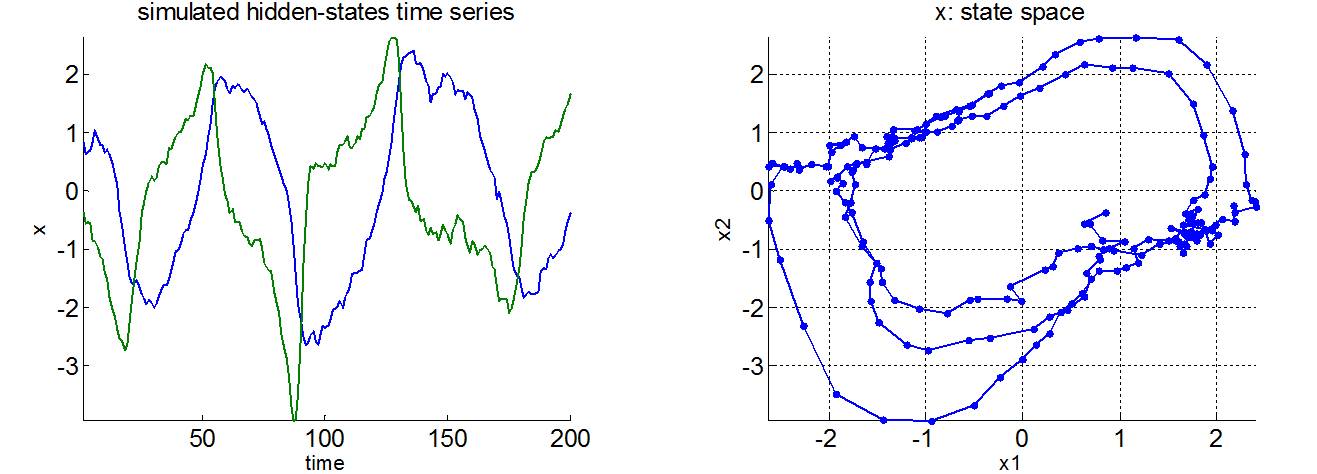
Double-well bistable system
The double-well potential system models a dissipative system, whose potential energy is a quartic (double-well) function of position. As a consequence, the system is bistable with two basins of attraction around two stable fixed points. In its deterministic variant, the system ends up spiralling around one or the other attractors, depending on its initial conditions and the magnitude of a damping force or dissipative term. Because we consider state-noise, the stochastic DCM can switch (tunnel) from one basin to the other, which leads to itinerant behaviour; this is why the double-well system can be used to model bistable perception. See demo_doubleWell.m.
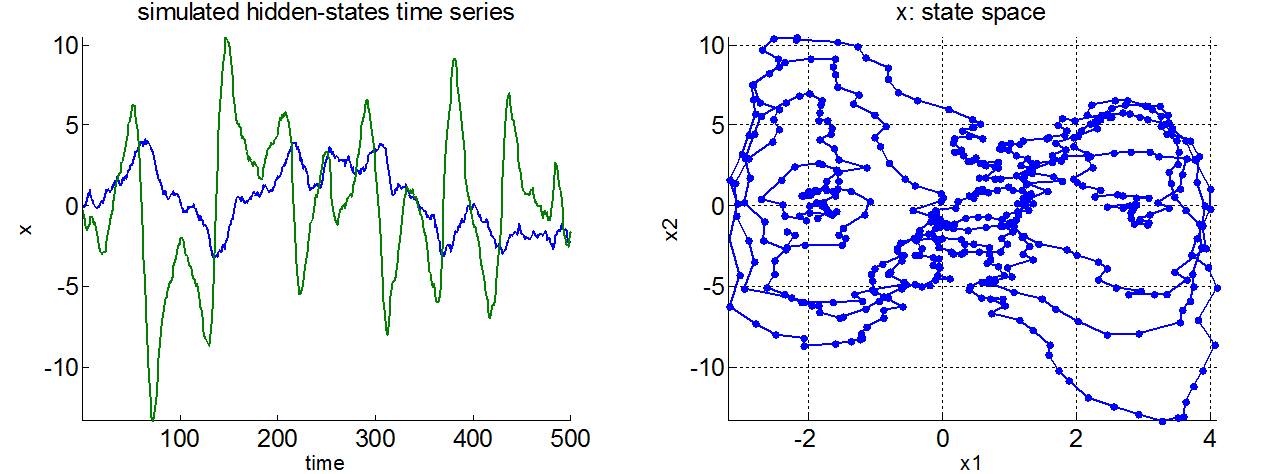
Rossler attractor
This is a model of a continuous-time dynamical system that exhibits chaotic dynamics associated with the fractal properties of the attractor. See demo_Rossler.m.
Henon map
This is one of the simplest discrete-time dynamical systems that exhibit chaotic behavior. See demo_Henon.m.